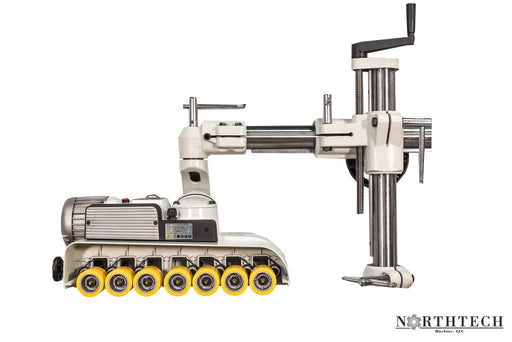
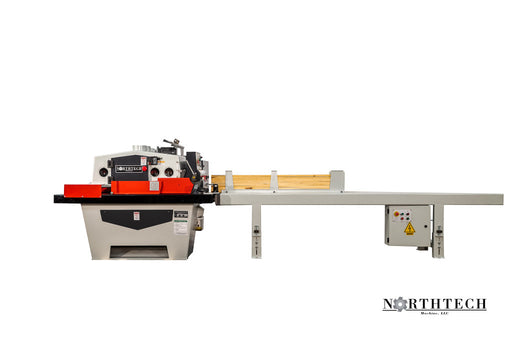
A feeder machine, also known as a stock feeder, is a vital component in industrial woodworking operations. Its primary function is to automate the feeding of workpieces into woodworking machinery such as saws, routers, and planers. Feeder machines enhance productivity by continuously and accurately feeding materials through the cutting or shaping process, reducing the need for manual labor and improving consistency in production.
Key Features of a Feeder
Variable Speed Control: Feeders come with adjustable speed settings to accommodate different material types, thicknesses, and cutting requirements.
Feeding Mechanism: Feeder machines utilize various feeding mechanisms such as rollers, belts, or pneumatic systems to grip and advance workpieces through the machinery.
Adjustable Pressure: Many feeders feature adjustable pressure settings to ensure optimal traction and stability when feeding different types of materials.
Compatibility: Feeder machines are designed to be compatible with a wide range of woodworking machinery, allowing for seamless integration into existing production lines.
Safety Features: Modern feeders are equipped with safety features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and safety interlocks to ensure operator safety during operation.
Applications of a Feeder
Rip Sawing: Feeders are used in rip sawing operations to continuously feed boards or panels through the saw blade for precise and consistent cuts.
Edge Banding: In edge banding processes, feeders automate the feeding of edge banding tape and workpieces through the edge banding machine, ensuring uniform application and trimming.
Planing and Thicknessing: Feeder machines assist in planing and thicknessing operations by feeding boards through planers and thicknessers, resulting in smooth and uniform thickness across the workpieces.
Moulding and Shaping: In moulding and shaping processes, feeders feed workpieces through moulders, shapers, and routers to create profiles, contours, and decorative elements.
Choosing the Right Feeder
Speed and Capacity: Consider the speed and feeding capacity of the feeder to ensure it can keep up with the production demands of your woodworking operation.
Feeding Mechanism: Choose a feeder with a feeding mechanism that is compatible with the materials and processes used in your woodworking applications.
Adjustability: Look for a feeder with adjustable speed, pressure, and feeding width settings to accommodate different workpiece sizes and cutting requirements.
Integration: Evaluate how the feeder integrates with your existing woodworking machinery and production processes to ensure seamless operation and compatibility.